Embed your learning content in a larger context. Here you will find step-by-step instructions on how to build a learning sequence according to the 5 E Learning Cycle.
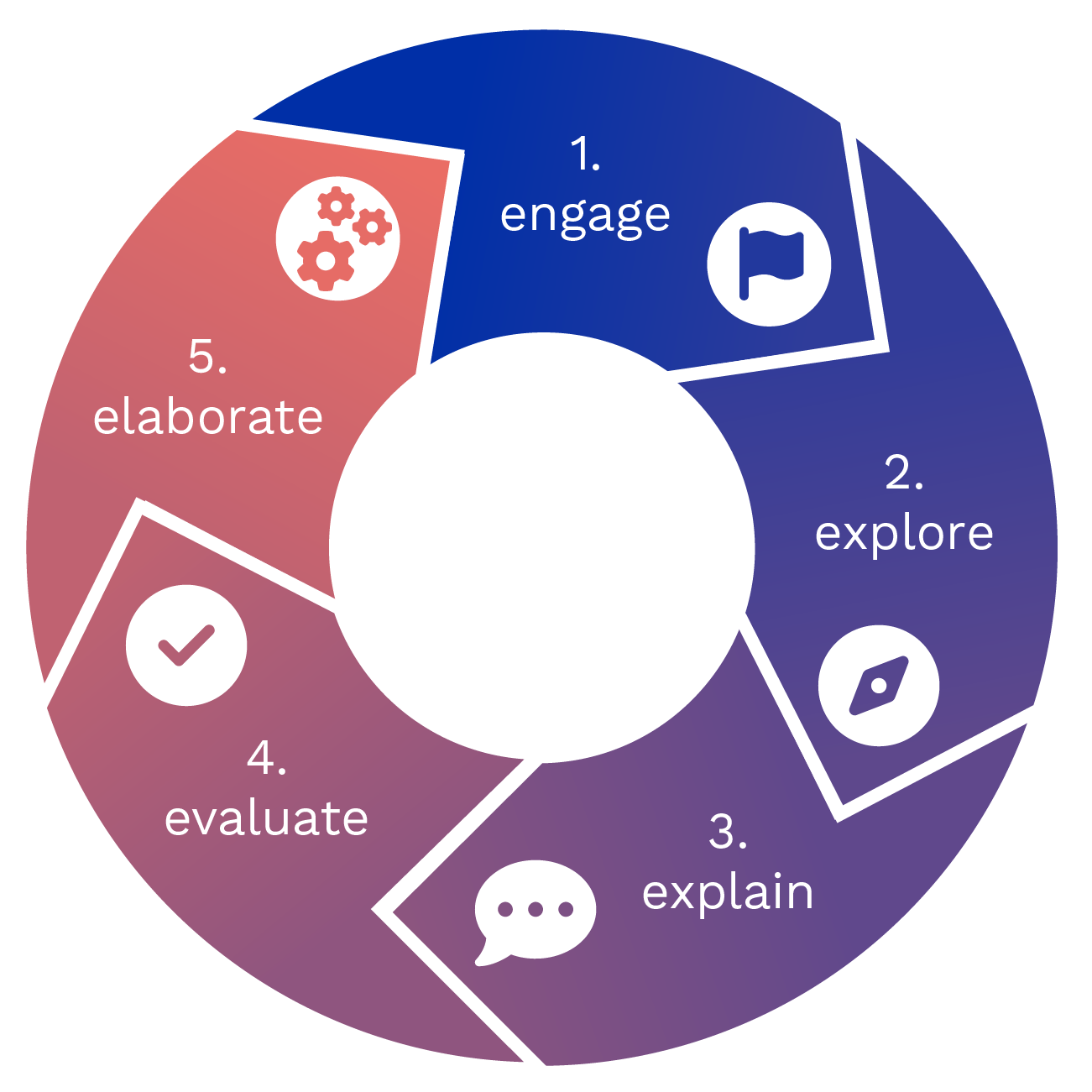
The 5 E Learning Cycle is based on the constructivist approach that learning is always an active reconstruction of information. This means that learners build new inputs on existing ideas, knowledge or experiences and combine them to create new information.
It consists of these 5 levels:
Note:
The 5-E model can be used for card decks as well as for engaging presentations with the Live feature and can be combined with active learning methods.
And this is how it works:
Choose a method to motivate learners for your deck or presentation:
Visual brainstorming
Short knowledge queries, e.g. definitions of terms, surveys
Video impulses on the topic, quotes
Reflect on everyday examples and personal experiences
Conduct comprehension questions, confirm/refute statements
Quiz, puzzle
Think-Pair-Share
(longest phase) Present your knowledge content here and incorporate interactive elements.
Informative cards with text or video
Quiz questions or surveys
Learners summarize the new information in their own words:
Have content summarized, e.g. ask comprehension questions with task cards
Allow students to reflect on content, e.g. with task cards or surveys
For interactive presentations: Use methods to ensure understanding such as Peer Instruction or Think-Pair-Share
Learners deepen, link, abstract, generalize or reflect critically
Transferring content to a different context
Work out connections
Work out differences and similarities
For interactive presentations: Have something designed by yourself
Learners check for themselves whether they can master the task:
Draw a conclusion
Have core statements formulated
Weigh up the pros and cons
Have your own position formulated
Display previously defined learning outcomes again and check whether they have been achieved
Note:
Depending on the learning content/scope, the individual phases of the 5 E cycle can be spread over a single deck or several decks in the case of self-learning.
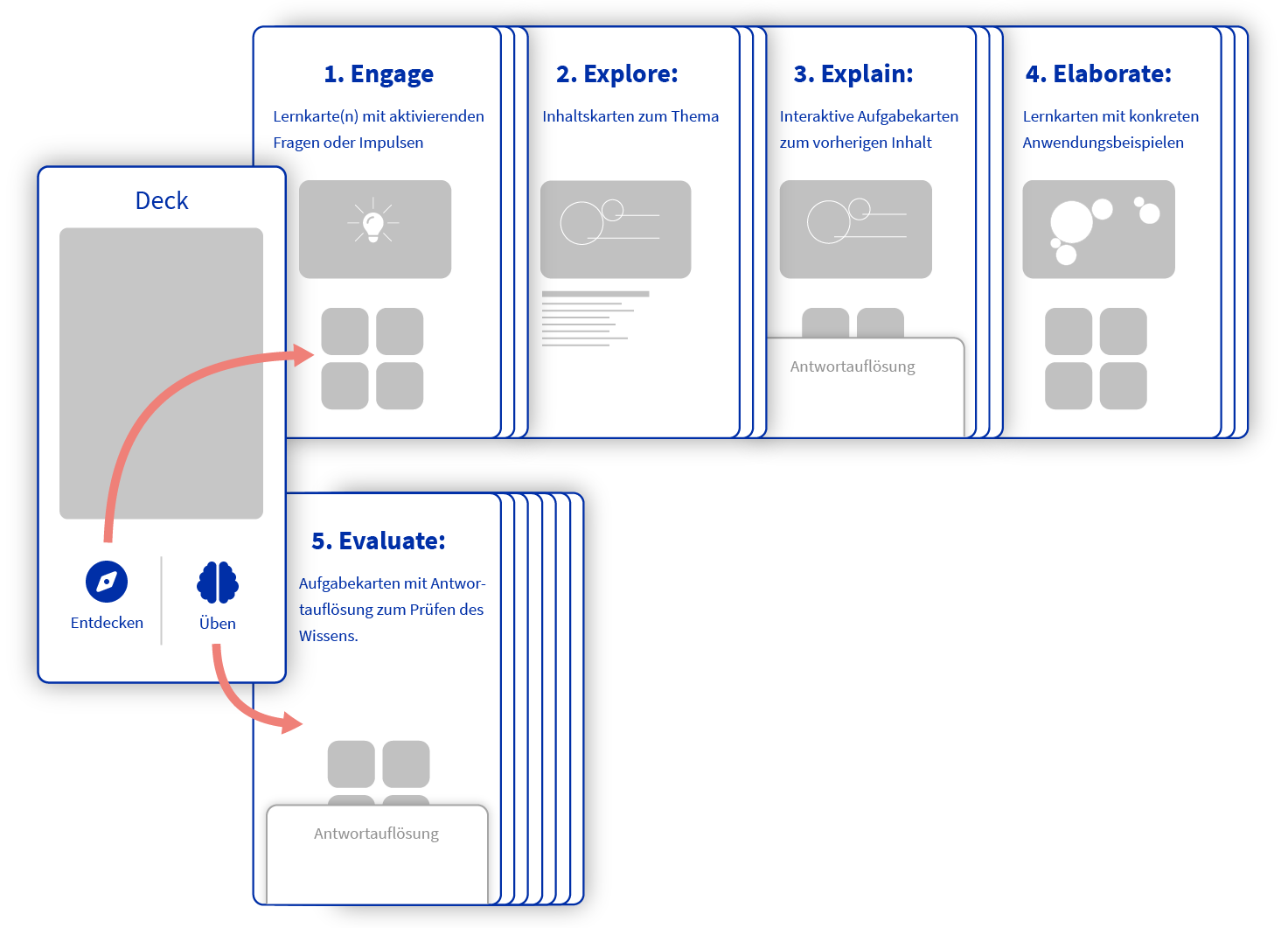
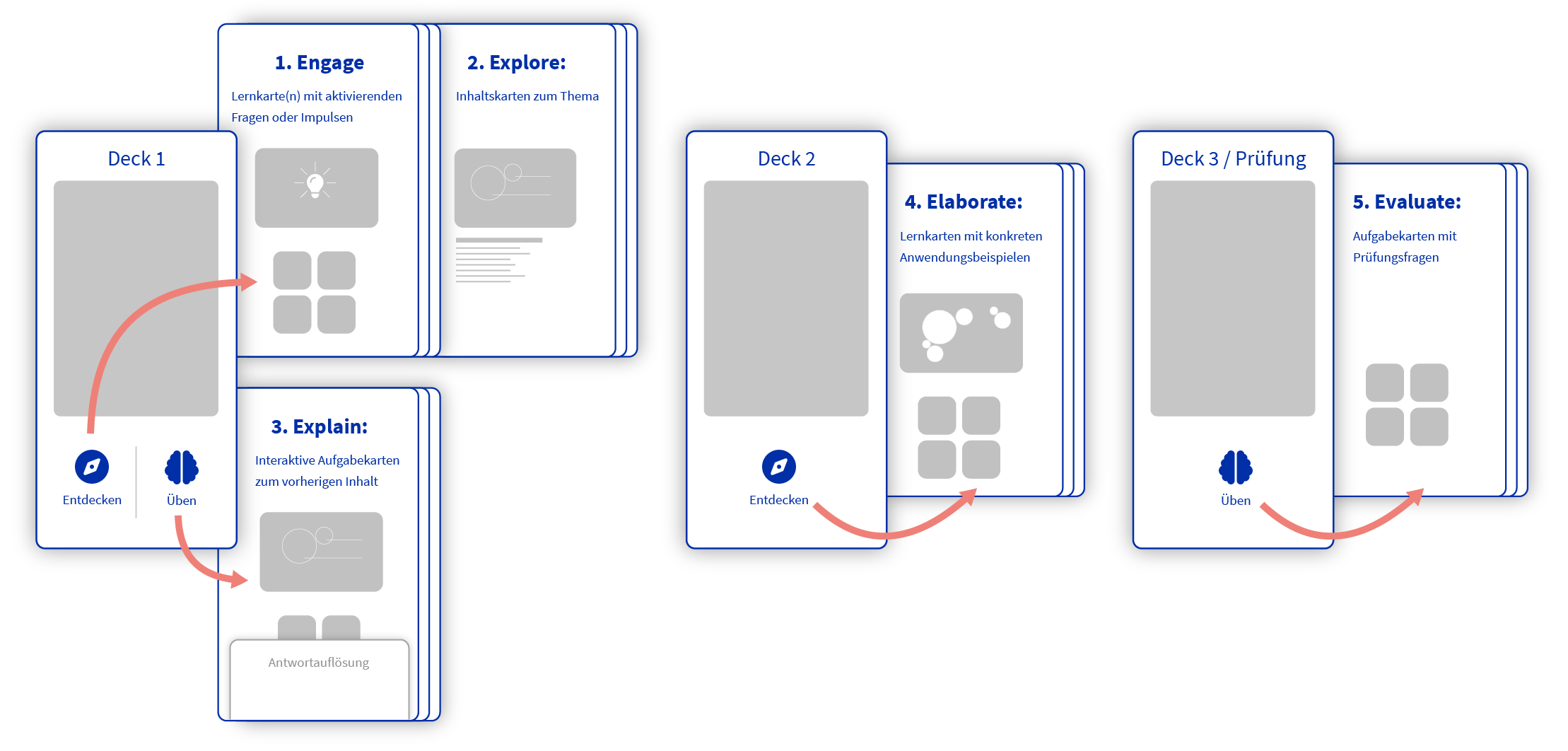
Note:
Learning is:
No passive storage but active construction of knowledge
Independent engagement with content, teacher = coach
Independent discovery of correlations
Previous chapter: > Step 3: Plan the learning activities
Next chapter: Use effective learning methods
More information:
Sources:
5E cycle: https://bscs.org/reports/the-bscs-5e-instructional-model-origins-and-effectiveness/